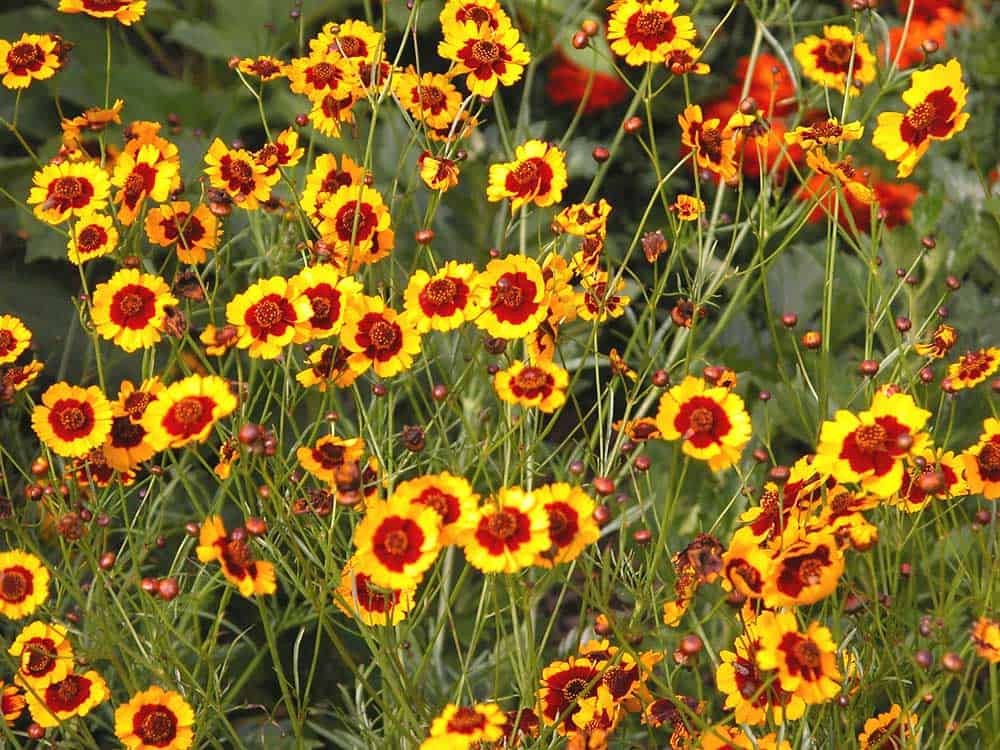
How Plains Coreopsis Colors Your World and Supports Ecosystems
Coreopsis tinctoria, commonly known as Plains Coreopsis or Golden Tickseed, is an annual flowering plant native to North America. A vibrant addition to native gardens, it offers striking yellow flowers with red centers from early summer to fall. This low-maintenance and drought-tolerant plant thrives in well-drained soils and attracts bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects.

It is crucial for at least 22 species of pollen specialist bees, including Pseudopanurgus and Agapostemon. It also serves as a host for moth larvae, such as the Wavy-Lined Emerald and Dimorphic Gray, and provides seeds for birds in winter. Historically used for medicinal purposes and dye production, Coreopsis tinctoria is both culturally significant and ecologically beneficial, making it a must-have for biodiversity-friendly gardens.
Gardening Uses and Benefits
Gardeners can greatly benefit from incorporating Coreopsis tinctoria into their native plant gardens:
- Ornamental Appeal: The plant produces showy masses of yellow flowers with red centers, adding a splash of color to gardens, wildflower meadows, and containers.
- Low Maintenance: It thrives in well-drained, sandy soils and can tolerate both full sun and partial shade, making it a versatile and easy-to-grow option.
- Extended Bloom Period: Coreopsis tinctoria blooms profusely from early summer through fall, providing continuous visual interest.
- Wildlife Attraction: The flowers attract a variety of pollinators, including bees, butterflies, and other beneficial insects, enhancing garden biodiversity.
Suggestions for Naturalistic Landscape Design
Coreopsis tinctoria can be effectively used in various naturalistic landscape designs:
- Wildflower Meadows: Planting Coreopsis tinctoria in wildflower meadows creates a vibrant, colorful display that attracts pollinators and supports local wildlife.
- Pollinator Gardens: Combining Coreopsis tinctoria with other pollinator-friendly plants like purple coneflower, Shasta daisy, and garden phlox enhances the garden’s biodiversity and visual appeal.
- Meadow Gardens: Pairing it with native grasses and other wildflowers such as Joe Pye weed, black-eyed Susan, and Shenandoah switchgrass creates a dynamic, naturalistic landscape.
- Borders and Edges: Use Coreopsis tinctoria along garden borders and edges to add a pop of color and attract beneficial insects.
- Containers and Small Spaces: This plant is also suitable for container gardening, making it a versatile choice for small gardens and patios.
Interesting Facts About Coreopsis tinctoria
- Cultural Significance: The plant is sometimes known as “calliopsis” in the horticultural trade.
- Medicinal Uses: Historically, Native Americans used the plant for medicinal purposes, such as treating diarrhea and internal pains.
- Dye Source: The plant was traditionally used to produce yellow and red dyes.
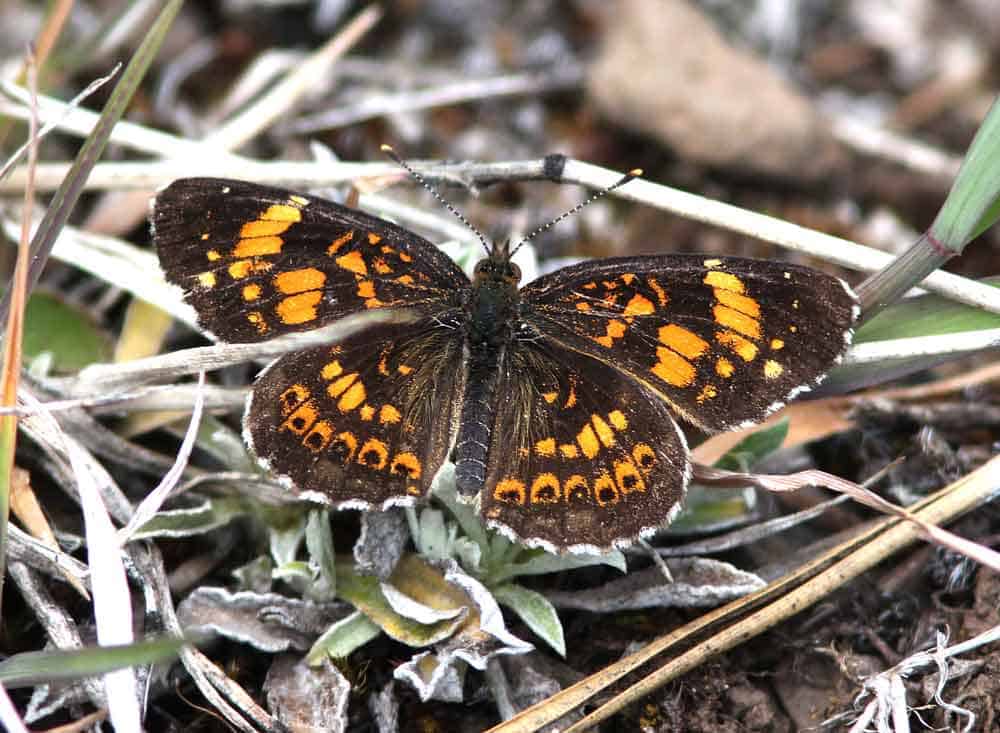

Specialist Relationships with Invertebrates and Other Animals
Coreopsis tinctoria has several specialist relationships that contribute to its ecological value:
- Pollinators: The flowers are a nectar source for native bees, butterflies, and other insects. Notable visitors include the silvery checkerspot butterfly (Chlosyne nycteis) and various native bee species like the green metallic sweat bees (Agapostemon spp.).
- Pollen Specialist Bees: Remarkably, Coreopsis tinctoria supports at least 22 species of pollen specialist bees. These include bees from the genera Pseudopanurgus and Agapostemon, which rely exclusively on the pollen from this plant for their nourishment and reproductive success. This makes Coreopsis tinctoria a critical resource for these bees, ensuring their survival and promoting pollination.
- Host Plant for Moths: The plant serves as a host for the larvae of several moth species, including:
- Wavy-Lined Emerald (Synchlora aerata): The caterpillars of this moth feed on the foliage of Coreopsis tinctoria.
- Dimorphic Gray (Tornos scolopacinarius): Another moth species whose larvae depend on Coreopsis tinctoria for their development.
- Calligrapha Californica: This species also uses Coreopsis tinctoria as a larval host plant.
- Birds: The seeds of Coreopsis tinctoria are a valuable food source for granivorous birds, especially during the winter months.
Ecosystem Contributions
Coreopsis tinctoria plays a significant role in promoting a healthy and biodiverse ecosystem:
- Soil Stabilization: Its root system helps stabilize soil, preventing erosion in disturbed areas such as roadsides and meadows.
- Habitat Provision: The plant provides habitat and food resources for a variety of pollinators and other beneficial insects, supporting local biodiversity.
- Seed Dispersal: Birds feeding on its seeds aid in the natural propagation and dispersal of the plant, contributing to its spread in the wild.
Header photo: “Texas bullnettle (Cindoscolus texanus) and plains coreopsis (Coreopsis tinctoria), Attwater Prairie Chicken National Wildlife Refuge” by William L. Farr is licensed under CC BY-SA 4.0.