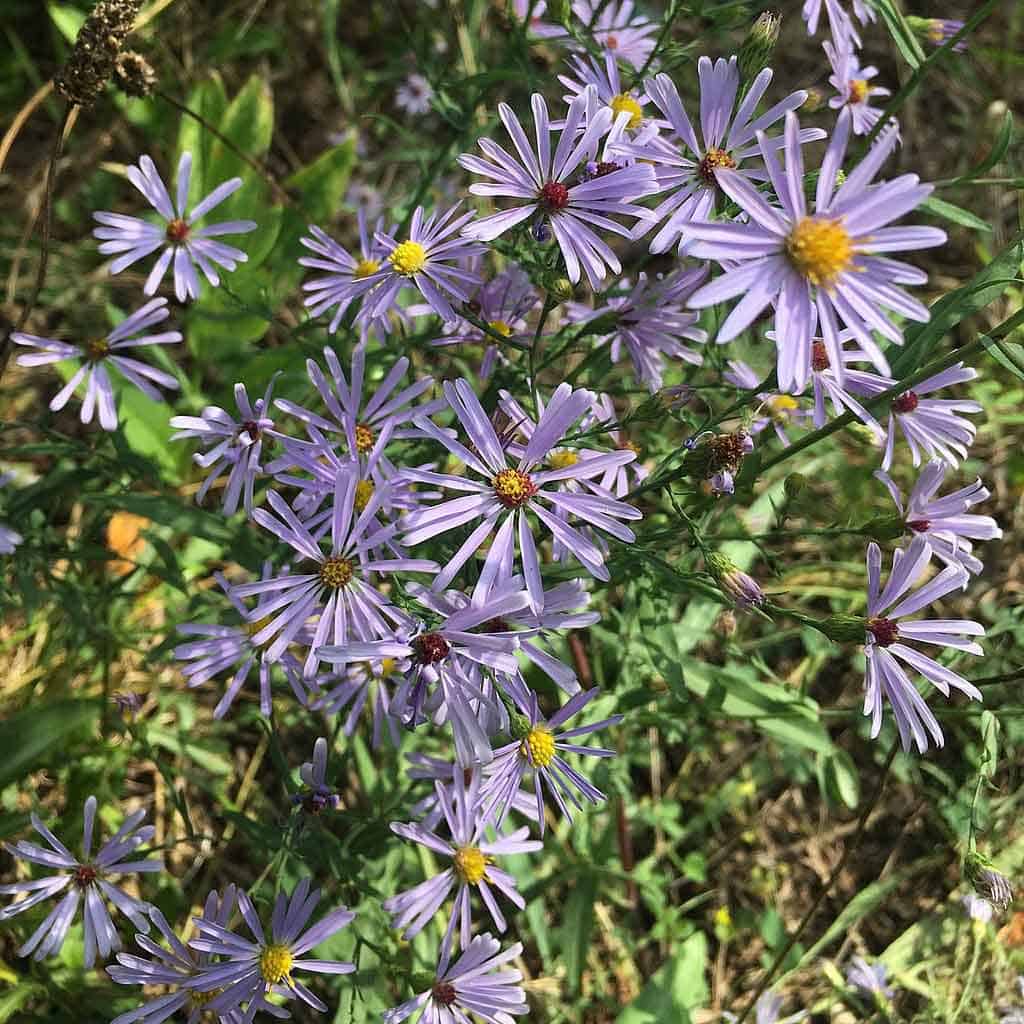
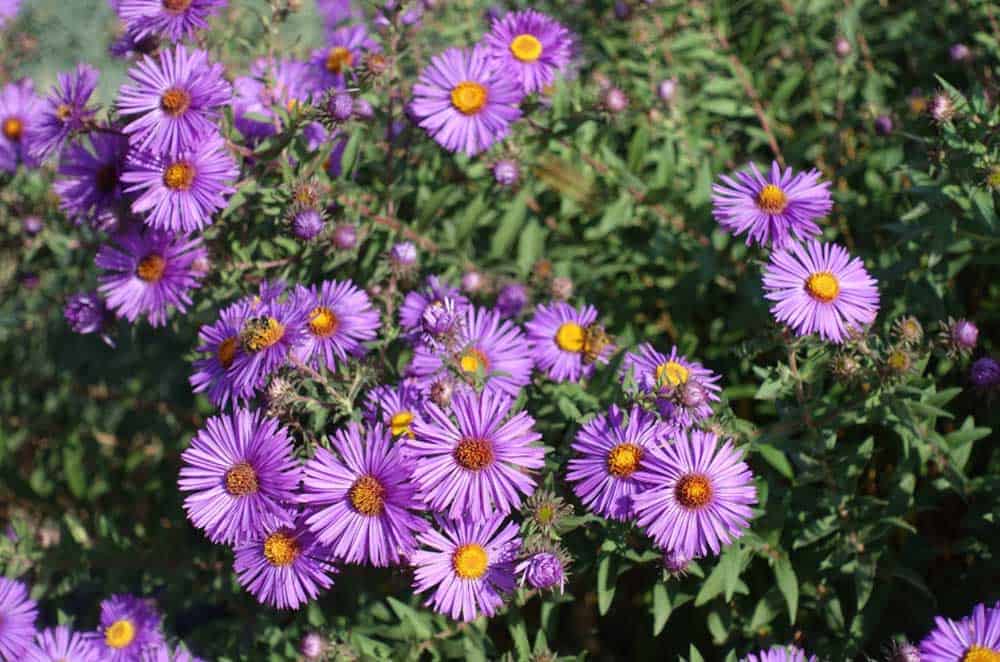
Symphyotrichum laeve, or Smooth Blue Aster, is a perennial plant native to North America, known for its vibrant blue flowers that bloom from late summer to fall. This species is a valuable addition to native plant gardens, offering a range of ecological benefits and aesthetic appeal.

Gardening Uses and Benefits
Smooth Blue Aster is a low-maintenance plant that thrives in well-drained soils and full sun to partial shade. It tolerates drought once established, making it suitable for water-wise landscapes.
The plant can be grown from seed, which requires cold stratification for optimal germination. Seeds should be planted in the fall to allow natural stratification over winter, and they germinate best with exposure to light.
For optimal growth, space plants about one square foot apart to allow for their 2-4 foot spread. To increase flower production and encourage bushier growth, plants can be cut back to 6 inches in late spring.
Companion plants that work well with Smooth Blue Aster include Echinacea purpurea (Purple Coneflower), Asclepias tuberosa (Butterfly Weed), Liatris aspera (Rough Blazing Star), and Solidago speciosa (Showy Goldenrod).

Native Range
Smooth Blue Aster is native to a wide range across North America, from British Columbia to Maine, south to Georgia, and west to New Mexico. It is commonly found in prairies, meadows, forest edges, and along roadsides.
Interesting Facts
- Smooth Blue Aster is known for its striking blue flowers, which are rare among native plants, providing a unique color contrast in gardens.
- This species is a member of the Asteraceae family, one of the largest families of flowering plants.
- It is highly adaptable and can tolerate a range of soil types, from sandy to clay, as long as they are well-drained.
Specialist Relationships with Invertebrates and Other Animals
Smooth Blue Aster plays a crucial role in supporting native pollinators. It is particularly important for specialist bees such as the Aster Mining Bee (Andrena asteris), which relies on asters for pollen. Additionally, the plant serves as a larval host for the Pearl Crescent butterfly (Phyciodes tharos), providing essential resources for its lifecycle. These relationships highlight the plant’s role in sustaining local biodiversity by supporting species that have co-evolved with it.
Ecosystem Contributions
The ecological contributions of Smooth Blue Aster extend beyond its role as a pollinator plant. It provides habitat and food for various insects and birds, contributing to the overall health of the ecosystem. By incorporating this species into a garden, gardeners can help restore natural habitats that have been fragmented by urban development. Its presence in a garden can enhance soil health and stability, promoting a resilient landscape that supports a diverse array of wildlife.