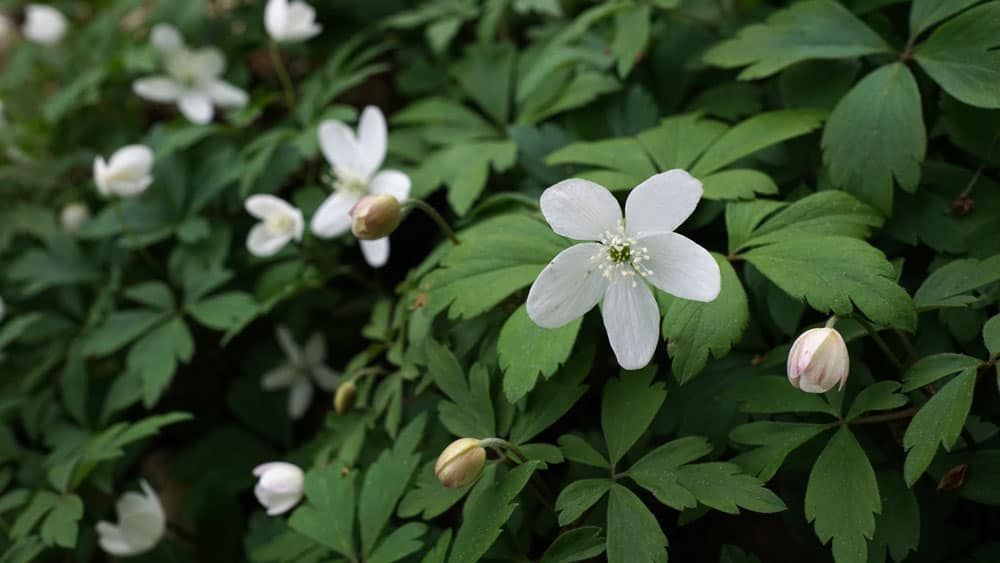
Woodland Wonder
The wood anemone (Anemone quinquefolia) or eastern windflower is a perennial, herbaceous wildflower native to the eastern and central United States. It typically grows 6-12 inches tall, with delicate, 5-petaled white flowers that bloom in early spring. The deeply lobed, trifoliate leaves form a basal rosette. The plant spreads by rhizomes to form colonies over time.

Wood anemones prefer partial shade to full shade conditions and moist, well-drained, humus-rich soils. They can tolerate a range of soil types but thrive in areas with high organic matter content. The plants go dormant in the summer after flowering and can re-emerge the following spring. They are native to most of the eastern and north central parts of the U.S. and are hardy in USDA Zones 4-8.
This native anemone is a popular choice for woodland, shade, and naturalistic gardens due to its early spring bloom, attractive foliage, and ability to spread into colonies. It provides visual interest and ground cover in shady areas where many other plants struggle. The delicate flowers also have ornamental appeal for native plant enthusiasts. The leaves of the wood anemone are sensitive to touch and will close inward when brushed or disturbed. This is an adaptive response to minimize water loss and deter herbivores.
The wood anemone provides food and habitat for a variety of native invertebrates. Its nectar and pollen attract early-season pollinators like bees, flies, and small butterflies. The leaves and flowers are also a larval host for specialist moths like the anemone moth (Fabriciana cydippe). Small mammals and birds may consume the seeds. Unlike many spring ephemerals that rely primarily on insect pollinators, Anemone quinquefolia is also known to be pollinated by small mammals, such as chipmunks and shrews, that may inadvertently transfer pollen while foraging on the nectar.
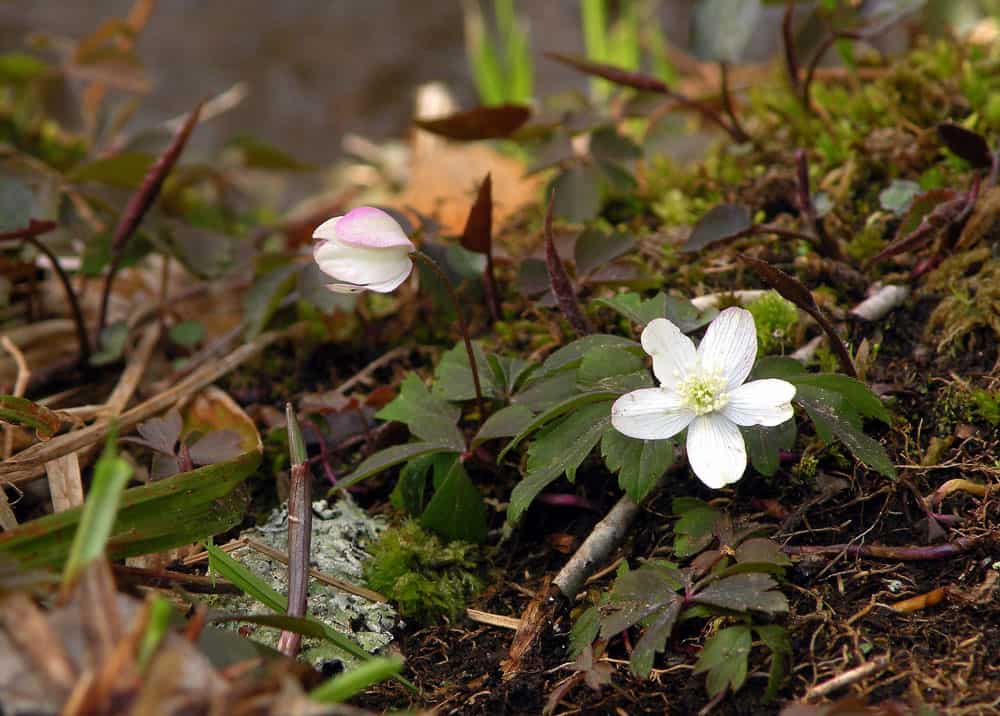

As a spring ephemeral, the wood anemone plays an important role in forest ecosystems by providing early-season forage and cover for insects, small vertebrates, and other wildlife when resources are scarce. Its spreading growth habit helps stabilize soils and prevent erosion in woodland understories. The decomposing plant matter also contributes to nutrient cycling.
Anemone quinquefolia is a valuable native plant for gardeners and ecosystems alike, offering aesthetic, ecological, and wildlife benefits through its distinct botanical characteristics and adaptations to shady, moist forest environments. Its popularity in the native plant trade reflects its versatility and importance in supporting biodiversity.